
The power consumption, depending on the intensity of the video card, is shown in the following graph and is measured according to the heat sink requirements (percentage of TDP). The following data shows the load of various components of the video card: so, you can see how much video memory is used (and also see the ratio of the minimum to the maximum on the graph), how busy the video card as a whole is (the graph corresponds to the first two indicators from the tab-core and memory frequencies), as well as its components, such as the memory controller or the bus interface.
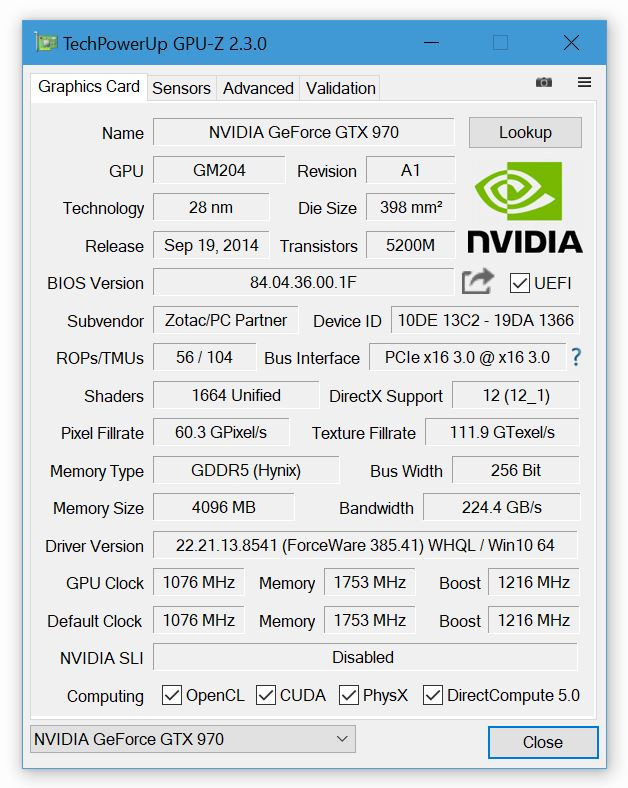
GPU-Z has the ability to track the speed of the cooler as a percentage of the maximum, and slightly lower-the speed of the fan in the usual revolutions per minute. To reduce the impact of hot air flows on the video card, manufacturers install a variety of coolers on the devices: in modern realities, you will not surprise anyone with three fans and cooling tubes together, on one video processor case. Carefully observe the temperature under load! Operating temperature - from 40 to 60 degrees Celsius, heating more than normal (from 65 degrees Celsius and above) is fraught with malfunctions (for example, distortion of the image on the screen) or even failure of the GPU. This is followed by information about the temperature of the video card. As a rule, the graphs in these two lines rise and fall in the same way. The graphs to the right of the data show the process of jumps in dynamics: so, when the red scale fills the bar to the very top, it means that the video card is running at the limit. The number of textures a graphics card can render per second.The first two values represent the current core and memory frequencies, respectively, at which the video processor is running. * For 55.7G Pixel / s, it processes 550 million pixels per second. The pixel fill rate is the number of pixels that the graphic engine can draw per second (the speed at which the drawing screen is accessed), and its performance depends on the number of GPU clocks and the number of ROPs (Render Output Pipelines) installed. The number of pixels a graphics card can render per second. When using GPGPU (stream processing) that uses GPU in addition to image processing such as Open CL and CUDA, the performance varies greatly depending on the number of shader units. The number of GPU cores is represented by the number of shading units that perform shading processing in 3D graphics. To save power, the graphics card automatically reduces speed and bandwidth when under load, and the after it indicates the current operating speed.
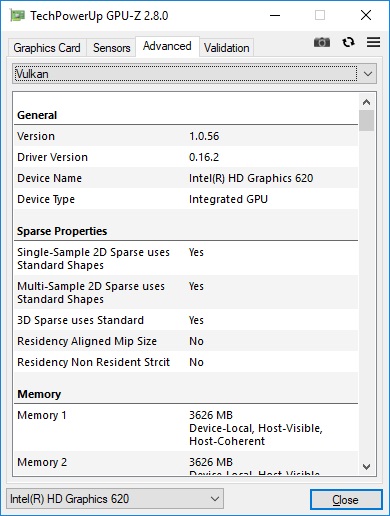
Represents the number of textures that can be processed. In 3D graphics, the method of pasting a texture on a polygon mesh (texture mapping) is generally used, and the texture mapping is processed by the TMU (Texture Mapping Unit), and the texture fill rate is 1 second.
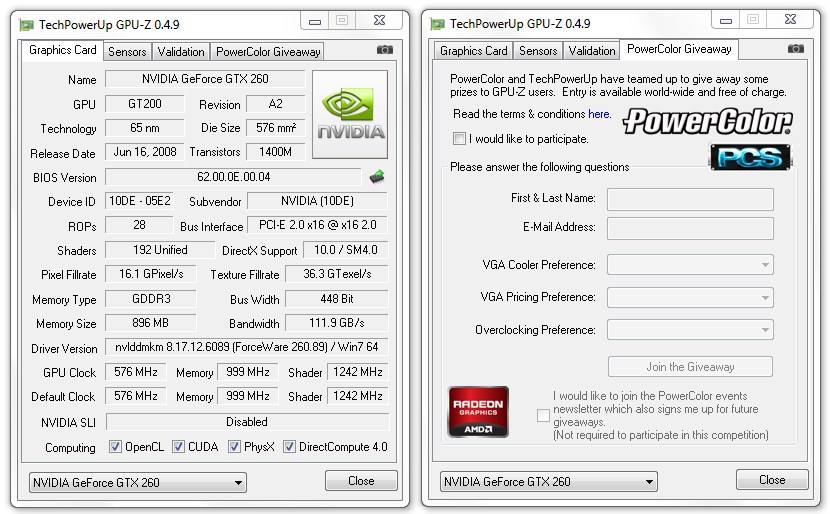
The number of Render Output Pipelines and Texture Mapping Units installed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
